When deciding to go abroad by adopting international diversification, firm faces two main problems. The first one is the global – local dilemma concerning the standardization level of its products and services, that should be customized between countries in order to meet local market requirements. The second is the business scope, that is, firms should concentrate their assets and production in some limited locations or spread in the world. Such asset and production concentration depends on the firm goal in accessing and exploiting local advantages of countries according to the principle of economy of scope. For example, the success of McDonald’s on the Champs Elysées in Paris, and the success of Pepsi and Coca-Cola worldwide are example of the global convergence of customer needs and tastes; when these groups provide standardized globally products by focusing on cost leadership advantage at international level.
Firms need to study and develop their international diversification in their own way for both (i) balancing the adaptation and standardization of their products, and (2) taking advantage and opportunities in different local markets on the basis of economies of scope. The differences between countries can be significant, and firms can offer a diverse range of products to adapt to each market. For example, Nokia built a mobile phone manufacturing factory in Vietnam for exploiting the potential of local labor as well as for targeting the local consumer market. The characteristics of the phone lines that Nokia offer in this target market are cheap and customized by such product type, which are suitable for Vietnamese preferences.
There are different reasons explaining why firms decide to pursue an internationalization strategy. The first group concerns the market, because of: market and competition globalization, following customers abroad, saturated domestic market, exploiting the differences between countries and regions (cultural, administrative, geographic, macro factors, especially technology). The second group consists in exploiting the advantages of strategic capacities and resources, including: globalization advantage, advantages of firms’ resources particularly in international markets, and for strengthening their position and market power. The third group of internationalization reasons concerns economic benefits, such as achieving the economy of scope, reducing risks, and offsetting profits between markets.
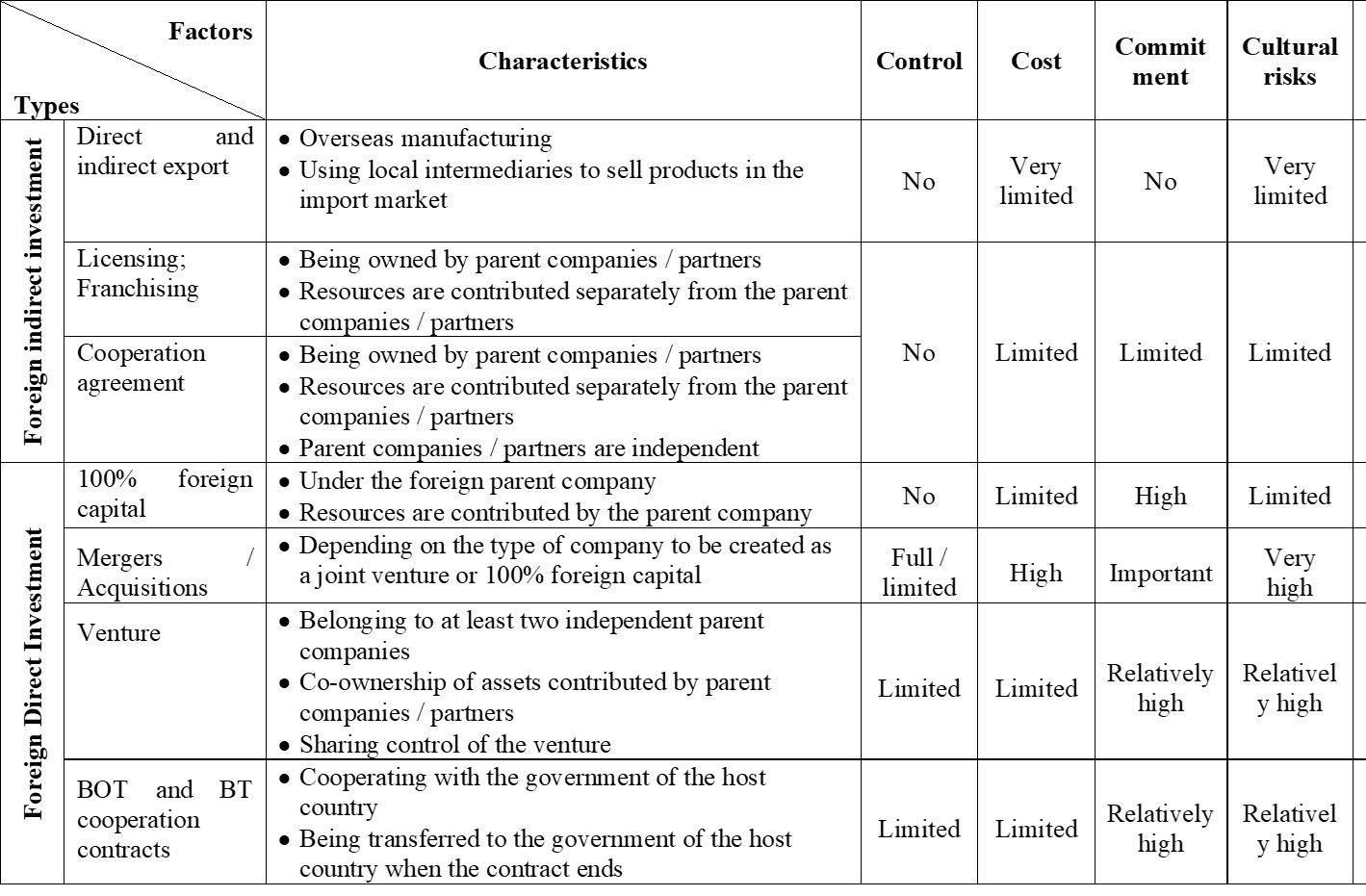
In the internationalization strategy, firms need to choose the right type of market entry. The advantages and disadvantages of different entry modes in foreign investments are summarized in the table below:
Table 1: Advantages and disadvantages of different entry modes in foreign investments

15 Jul 2020
15 Jul 2020
15 Jul 2020
10 Sep 2019